Counting cells- fast, objective, reproducible - do it with us!
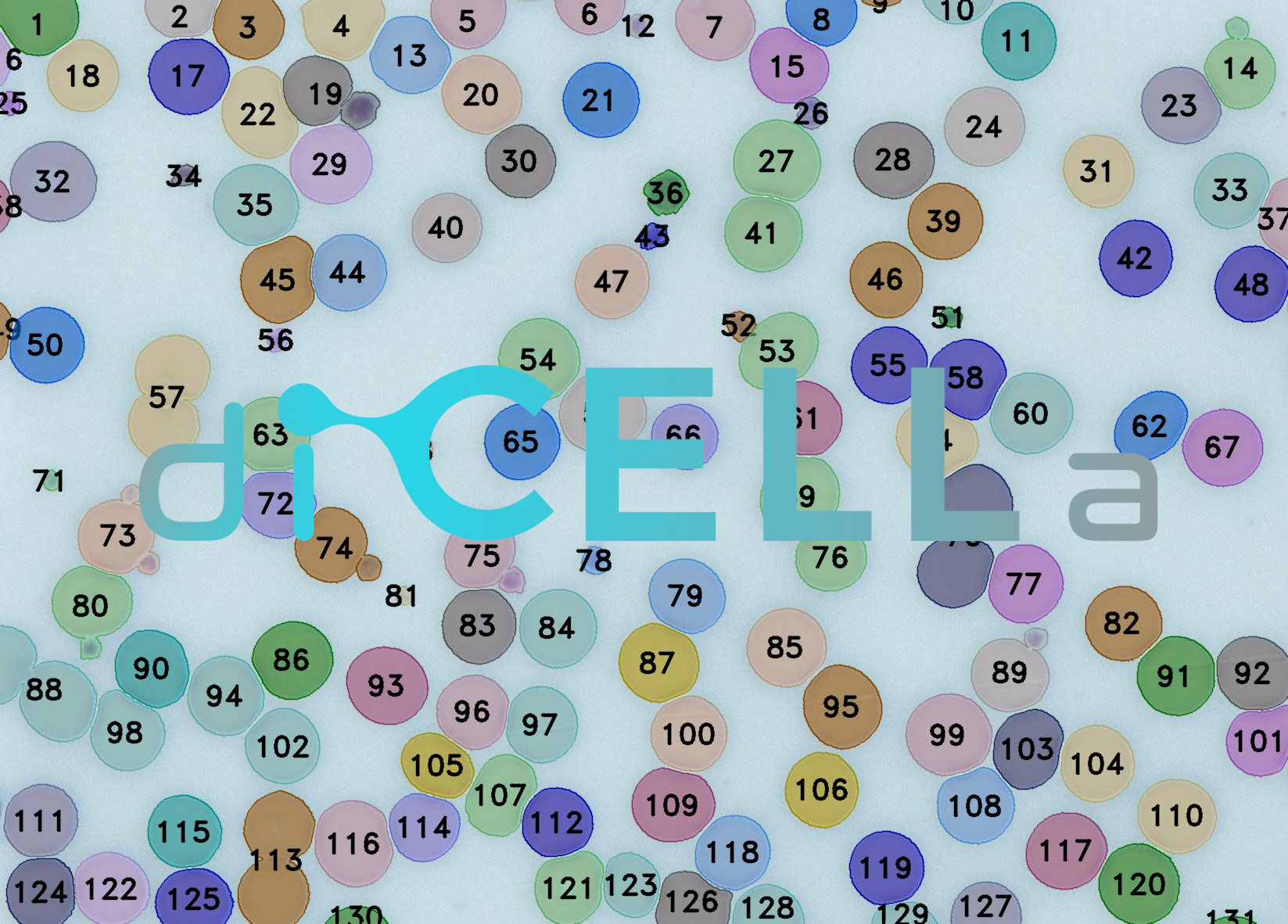
application for fast, objective,
reproducible cell counting
diCELLa Counting SYSTEM is an application that allows you to quickly analyze results of your experiment. Given only unmodified images our algorithm counts cells visible in the image.
Our solution:
- allows to analyze a wide range of images coming from different imaging devices,
- provides you with results in under a minute.
diCELLa Counting SYSTEM is fast, automatic, reliable and most of all helps you avoid time-consuming and not always ideal manual counting.
How to use it?
To use the diCELLa Counting SYSTEM you need to upload a number of images (max. size 7MB per image) in any image format. The software works on images taken using light microscope.
Results are available to download in txt or pdf format just few seconds after running the experiment in Image Service. They consist of statistics with number of cells visible in the image, input image and output image with marked cells.
Create an account on our Image Service platform, buy dicellons and exchange them to upload your images.
If you want to use your results in a scientific paper or during a speech at a scientific conference, contact us to get a discount!
Scientific Background
Cell counting is a standard, daily procedure in laboratories with numerous application in diagnostics and scientific research. Such an indicator might be helpful in determining the state of cell culture development, bacteria proliferation and pathology detection [1-2]. For instance analysis of blood smear images, based on cell counting, plays a vital role in the field of medicine as it helps to diagnose the disease at the early stage [6]. It provides support for the doctors to take the right decision of monitoring and in result, prevention of the disease.
After acquiring image from microscope is necessary to define number of cells [1]. Usually, a hemocytometer is used to perform this task. This method, however, has many disadvantages and it's likely to be inaccurate, due to limited counting area. Farther, intersections of lines heavily contribute to false positives [4]. Moreover, the manual counting is tedious likewise time-consuming [3-5]. It also puts under stress medical laboratory technicians which has an influence on erroneous results. A commercial cell counter may provide considerable improvement, but the cost of the instrument and consumables are high [4].
Automatic operations using sophisticated algorithms allows to solve those problems. First, the area captured by the camera is larger than the suggested areas for manual cell counting, thus encompassing a larger cell population. It also helps to avoid a problem with different cell density in observed field [4]. It is proved that this approach demonstrates a key advantage of consistency, as well as simplicity, accuracy, and speed, and poses an important question with regard to the reliability of manual cell counting at low cell concentrations [6].
References:
[1] Özkan A., İşgör S. B., Tora H., Uyar P. and İşcan M.:"An alternative method for cell counting," 2011 IEEE 19th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, 2011,pp.1048-1051.
[2] Shapiro MF., Greenfield S.: „Diagnostic Decision: The Complete Blood Count and Leukocyte Differential Count: An Approach to Their Rational Application.” Ann Intern Med.; 106:65–74. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-1-65
[3] Tulsani H., Gupta R. and Kapoor R.: "An improved methodology for blood cell counting", IMPACT-2013, Aligarh, 2013, pp. 88-92.
[4] Grishagin I. V.: „Automatic cell counting with ImageJ”, Analytical Biochemistry, Volume 473, 2015, Pages 63-65
[5] Sizto N. L., Dietz L. J.: „Method and apparatus for cell counting and cell classification”, US patent 5,556,764, Sep. 17, 1996
[6] Acharya, V., & Kumar, P. (2017). Identification and red blood cell automated counting from blood smear images using computer-aided system. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 56(3), 483–489. doi:10.1007/s11517-017-1708-9
